Curriculum, Instruction, and Assessment
.jpg)
Formative Assessment Ideas (Flipbook / Powerpoint)
Confused vs Clarified Learning Objectives
Confused Learning Objective | Clarified Learning Objective | Context of Learning |
|---|---|---|
| To be able to write instructions on how to change a bicycle tire. | To be able to write clear instructions. | Changing a bicycle tire. |
| To be able to present an argument for or against assisted suicide. | To be able to present an argument either for or against an emotionally charged proposition. | Assisted suicide. |
| To know what the local priest does. | To know the duties and responsibilities of religious leaders. | The local priest. |
| To produce and analyze a questionnaire about movie-going habits. | To construct and analyze questionnaire data. | Movie-going habits. |
| To design an experiment to find out what conditions pill bugs prefer. | To design fair tests for scientific questions. | The preferred habitat of pill bugs. |
Assessment Planning Resources
Part One - Unit Planning
Part Two Project/Activity Planning
ENGLISH | FRENCH | EXAMPLE |
|---|---|---|
| Lesson Plan Template Grid Lesson Plan Template Simple | Lesson Plan Template Grid FR Lesson Plan Template Simple FR | Lesson Plan Template Grid EX Lesson Plan Template Simple EX |
Part Three - Assessment
ENGLISH | FRENCH | EXAMPLE |
|---|---|---|
Ongoing Student Self-Reflection EX |
BC Curricular Rubrics
Please visit the BC Curriculum Website to view and download the curricular rubrics.
Class Profile
A class profile provides a snapshot of the class’s strengths, challenges, class-wide goals, and individual needs.
Teachers can develop a student dimension inventory (see template) that captures students' specific interests, strengths, necessary supports, and targeted core competencies. This tool is useful in guiding both instruction and assessment strategies.
Strength-Based Comments
Strength-based comments emphasize what students have learned or achieved, identifying strengths and offering specific examples to clarify general statements. These comments align with learning standards, frame difficulties as challenges, and suggest actionable next steps for improvement.
 Response to Intervention - Tier 1,2,3
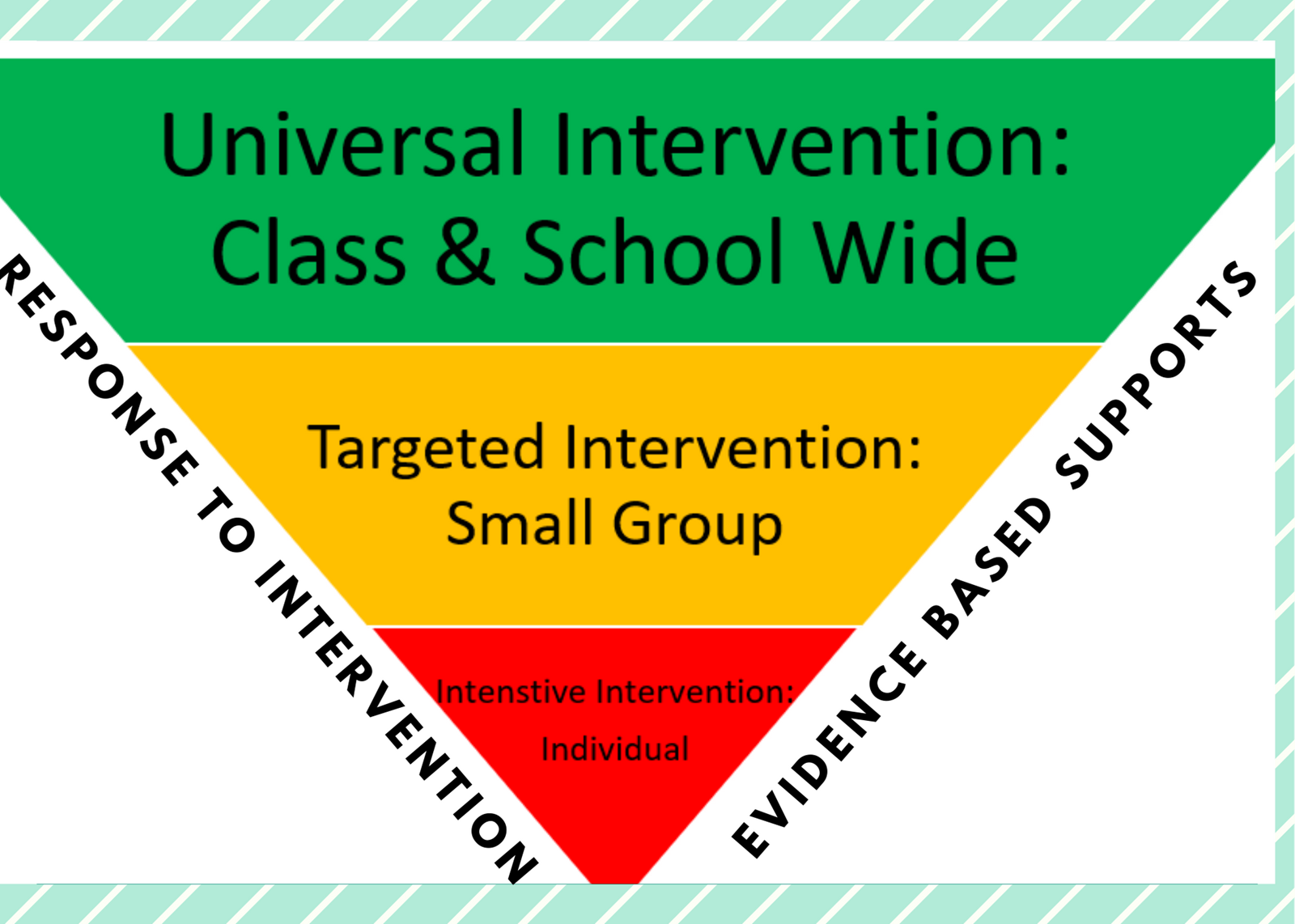
Response to Intervention - Tier 1,2,3
Response to Intervention (RTI) is a multi-tiered system of support for all learners, particularly those in need of support. Ultimately, RTI is a school-wide prevention system that focuses on identifying, teaching and monitoring students experiencing difficulties.
Types of Communicating Student Learning
 Point of Contact
Point of Contact
These are scheduled points when teachers share specific updates on a student’s progress. Communication should clearly explain how the student is performing relative to the course or subject, using the provincial proficiency scale. Formats can include:
- Teacher-created rubrics
- Portfolios
- Emails
- Phone calls
 Student Learning Conferences
Student Learning Conferences
Student Learning Conferences involve teachers, students, and parents collaborating to showcase the student’s progress. These meetings help parents understand their child’s overall development and achievements.
 MyEd BC Written Reports
MyEd BC Written Reports
Throughout the year, Written Learning Updates and the Summary of Learning will be shared via MyEdBC.
- Elementary and middle schools will provide two Learning Updates, followed by a Summary of Learning at the end of the school year.
- Secondary schools will issue one Learning Update midway through each semester and a Summary of Learning at the semester's end.
Triangulate Evidence of Student Learning
Conversations | Products | Observations |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
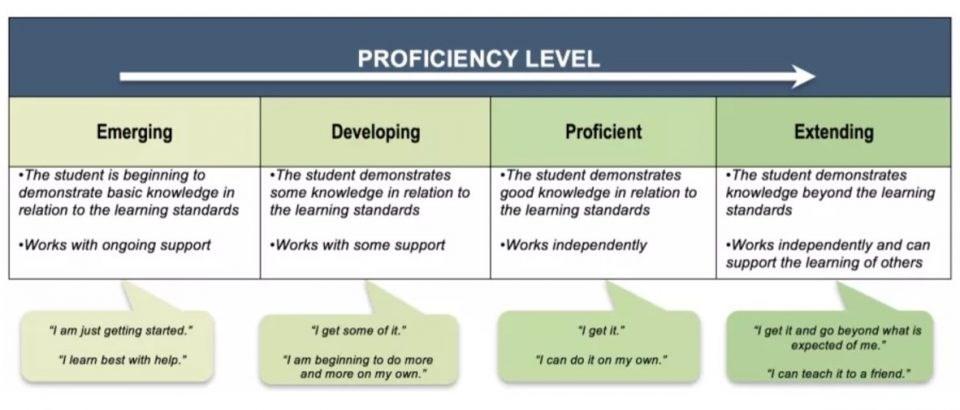
Provincial Proficiency Scale
The four-point Provincial Proficiency Scale is used to communicate student learning in all areas of learning. It is a requirement for student reporting in Grades K-9 as well as for the secondary Literacy and Numeracy Assessments. The four points on the scale include Emerging, Developing, Proficient, and Extending.
Graduation Assessments
Literacy Assessments - Grades 10 and 12
The Literacy Assessment is a provincial assessment that assesses student proficiency in literacy. It is a graduation requirement and is completed by students in grades 10 and 12.
The Literacy Assessment assesses students’ ability to use critical and reflective thinking and analysis to make meaning from a diverse array of texts. It also assesses the ability of students to communicate their ideas or those found in the texts. The assessment is not based on a particular subject matter or course, but rather on learning across multiple subjects from kindergarten to Grade 12.
Learn more about the secondary assessments by visiting the Provincial Assessment page.
Grade 10 Numeracy Assessment
The Grade 10 Numeracy Assessment is a provincial assessment that assesses student proficiency in numeracy. It is a graduation requirement and students take the assessment in their Grade 10 year. The Grade 10 Numeracy Assessment focuses on the application of mathematical concepts learned across multiple subjects from kindergarten to Grade 10. It requires students to solve problems by using five numeracy processes (different ways of thinking and working): interpret, apply, solve, analyze and communicate.
Learn more about the Grade 10 Numeracy assessment by viewing the Grade 10 Numeracy Assessment Quick Fact Sheet.